Introduction:
Migrating databases, especially between different systems like SQL Server and PostgreSQL, is a critical task for many organizations. Whether it's for modernization, cost reduction, or leveraging PostgreSQL's capabilities, a reliable migration strategy is essential. This guide focuses on using pgloader, a powerful open-source tool, to facilitate this process, while incorporating current best practices and technology considerations.
To continue our migration series, today’s post will focus on pgloader. Pgloader is another Open Source data migration utility for PostgreSQL from MySQL and SQL Server. Today’s demo will migrate a sample database (StackOverflow) from MS SQL Server 2019 to Postgresql v10.
Why Migrate from SQL Server to PostgreSQL?
Organizations choose to migrate for various reasons:
- Cost Optimization: PostgreSQL's open-source nature eliminates expensive licensing fees.
- Enhanced Flexibility: PostgreSQL offers extensibility and adherence to SQL standards.
- Advanced Features: PostgreSQL boasts features like advanced data types, concurrency control, and GIS support.
- Open Source Community: Benefit from a vibrant and active community.
Introducing pgloader: Your Migration Workhorse
pgloader is a versatile tool designed to efficiently migrate data from various sources, including SQL Server, to PostgreSQL. It offers features like:
- Data Type Conversion: Automatic or customizable data type mapping.
- Parallel Loading: Improved performance through parallel data transfer.
- Schema Transformation: Flexibility in schema and table transformations.
- Minimal Downtime: Strategies to minimize disruption during migration.
Prerequisites:
- PostgreSQL: Ensure a PostgreSQL server is set up and accessible. (Consider PostgreSQL 14 or later for performance and features)
- SQL Server: Have access to the SQL Server instance you want to migrate. (SQL Server 2016 or later)
- pgloader: Install pgloader on your system. (Installation methods vary by OS; refer to the official pgloader documentation for the latest instructions. Typically, it involves package managers or building from source.)
- FreeTDS (if needed): If connecting from a Linux/Unix system to SQL Server, FreeTDS might be required for the connection. (Installation via your system's package manager is recommended.)
Migration Workflow
-
Planning is Paramount:
- Assess your SQL Server database: Identify tables, data types, relationships, and dependencies.
- Define your PostgreSQL schema: Plan how the data will be structured in PostgreSQL.
- Choose a migration strategy: Full migration, incremental migration, or hybrid.
- Develop a rollback plan: Outline steps to revert to SQL Server if necessary.
- Estimate downtime: Plan for minimal disruption to your applications.
-
Configuration:
- pgloader command file: Create a command file to specify the source (SQL Server) and target (PostgreSQL) connections, table mappings, and any transformations.
- FreeTDS configuration (if applicable): Configure FreeTDS to connect to your SQL Server instance.
-
Example Migration (Conceptual):
- Connect: Establish connections to both SQL Server and PostgreSQL.
- Schema transformation: (Example: Rename schemas or adjust table names)
- Data migration: pgloader efficiently transfers data from SQL Server to PostgreSQL.
- Data type conversion: pgloader handles (or you configure) how data types are mapped.
- Index creation: Recreate indexes in PostgreSQL for optimal performance.
- Constraint creation: Recreate primary keys, foreign keys, and other constraints.
-
Verification:
- Data validation: Compare row counts and data integrity between SQL Server and PostgreSQL.
- Application testing: Test your applications with the PostgreSQL database.
- Performance testing: Ensure PostgreSQL meets your performance requirements.
-
Cutover:
- Minimize downtime during the switch.
- Monitor the PostgreSQL database closely after cutover.
StackOverflow contains the following tables
1> use [StackOverflow] 2> go Changed database context to 'StackOverflow'. 1> select name from sys.tables order by name 2> go --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Badges Comments LinkTypes PostLinks Posts PostTypes Users Votes VoteTypes (9 rows affected)
- Install pgloader – on ubuntu this is a simple apt-get install pgloader but you can also build from source
- Pglolader uses the FreeTDS driver (on RedHat I needed to install the following freetds freetds-libs freetds-common)
- Pgloader has multiple options
# pgloader pgloader [ option ... ] command-file ... pgloader [ option ... ] SOURCE TARGET --help -h boolean Show usage and exit. --version -V boolean Displays pgloader version and exit. --quiet -q boolean Be quiet --verbose -v boolean Be verbose --debug - boolean Display debug level information. --client-min-messages string Filter logs seen at the console (default: "warning") --log-min-messages string Filter logs seen in the logfile (default: "notice") --summary -S string Filename where to copy the summary --root-dir -D string Output root directory. (default: #P"/tmp/pgloader/") --upgrade-config -U boolean Output the command(s) corresponding to .conf file for v2.x --list-encodings -E boolean List pgloader known encodings and exit. --logfile -L string Filename where to send the logs. --load-lisp-file -l string Read user code from files --dry-run boolean Only check database connections, don't load anything. --on-error-stop boolean Refrain from handling errors properly. --no-ssl-cert-verification boolean Instruct OpenSSL to bypass verifying certificates. --context -C string Command Context Variables --with string Load options --set string PostgreSQL options --field string Source file fields specification --cast string Specific cast rules --type string Force input source type --encoding string Source expected encoding --before string SQL script to run before loading the data --after string SQL script to run after loading the data --self-upgrade string Path to pgloader newer sources --regress boolean Drive regression testing
- Create the database in postgres – add the uuid-ossp extension
postgres=# create database stackoverflow owner btpg10; CREATE DATABASE postgres=# \c stackoverflow btpg10; You are now connected to database "stackoverflow" as user "btpg10". stackoverflow=# create extension "uuid-ossp"; CREATE EXTENSION
- I define a parfile for specific flags – we can alter table names, exclude tables, define data type conversions - for this demo we will only define our source/target connections and rename the default MS SQL schema(dbo) to the default postgres (public)
load database from mssql://SA:@host1:1433/StackOverflow into postgresql://btpg10:@host2:5432/stackoverflow alter schema before load do $$ drop schema if exists dbo cascade; $$;
- Define freetds config file in same directory
# view .freetds.conf [global] tds version = 7.4 client charset = UTF-8
- Test connectivity
# pgloader --dry-run ss_so.cmd
2020-06-25T18:33:26.014000Z LOG pgloader version "3.6.1"
2020-06-25T18:33:26.058000Z LOG Loading the FreeTDS shared librairy (sybdb)
2020-06-25T18:33:26.061000Z LOG DRY RUN, only checking connections.
2020-06-25T18:33:26.062000Z LOG Attempting to connect to #<MSSQL-CONNECTION mssql://SA@10.98.0.13:1433/StackOverflow {100696F6F3}>
2020-06-25T18:33:26.190000Z LOG Success, opened #<MSSQL-CONNECTION mssql://SA@10.98.0.13:1433/StackOverflow {100696F6F3}>.
2020-06-25T18:33:26.190000Z LOG Running a simple query: SELECT 1;
2020-06-25T18:33:26.210000Z LOG Attempting to connect to #<PGSQL-CONNECTION pgsql://btpg10@10.99.100.9:5432/stackoverflow {1006970C13}>
2020-06-25T18:33:26.244000Z LOG Success, opened #<PGSQL-CONNECTION pgsql://btpg10@10.99.100.9:5432/stackoverflow {1006970C13}>.
2020-06-25T18:33:26.245000Z LOG Running a simple query: SELECT 1;
2020-06-25T18:33:26.245000Z LOG report summary reset
table name errors rows bytes total time
-------------- ---------- -------- --------- --------------
-------------- ---------- -------- --------- --------------
- Run data migration
# pgloader --verbose ss_so.cmd
2020-06-25T18:42:07.745000Z LOG report summary reset
table name errors read imported bytes total time read write
----------------------- --------- --------- --------- --------- -------------- --------- ---------
before load 0 1 1 0.017s
fetch meta data 0 18 18 0.457s
Create Schemas 0 0 0 0.001s
Create SQL Types 0 0 0 0.009s
Create tables 0 18 18 0.102s
Set Table OIDs 0 9 9 0.006s
----------------------- --------- --------- --------- --------- -------------- --------- ---------
public.badges 0 1102019 1102019 50.5 MB 10.400s 10.396s 6.802s
public.comments 0 3875183 3875183 743.1 MB 1m32.008s 1m32.002s 58.180s
public.postlinks 0 161519 161519 7.5 MB 1.709s 1.700s 1.111s
public.posttypes 0 8 8 0.1 kB 0.143s 0.137s
public.votes 0 10143364 10143364 424.5 MB 1m38.394s 1m37.466s 1m6.057s
public.linktypes 0 2 2 0.0 kB 0.132s 0.130s
public.posts 0 3729195 3729195 2.8 GB 5m8.075s 5m8.051s 2m37.241s
public.users 0 299398 299398 42.7 MB 12.007s 5.144s 4.256s
public.votetypes 0 15 15 0.2 kB 0.134s 0.131s
----------------------- --------- --------- --------- --------- -------------- --------- ---------
COPY Threads Completion 0 4 4 6m52.193s
Create Indexes 0 9 9 41.768s
Index Build Completion 0 9 9 4.211s
Reset Sequences 0 9 9 0.443s
Primary Keys 0 9 9 0.067s
Create Foreign Keys 0 0 0 0.000s
Create Triggers 0 0 0 0.002s
Install Comments 0 0 0 0.000s
----------------------- --------- --------- --------- --------- -------------- --------- ---------
Total import time ✓ 19310703 19310703 4.1 GB 7m38.684s
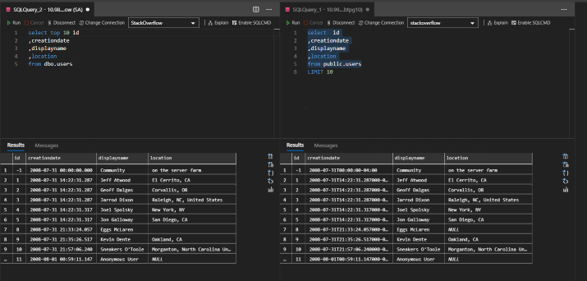
- Verify tables / data in Postgresql
postgres=# \c stackoverflow You are now connected to database "stackoverflow" as user "postgres". stackoverflow=# \dt List of relations Schema | Name | Type | Owner --------+-----------+-------+-------- public | badges | table | btpg10 public | comments | table | btpg10 public | linktypes | table | btpg10 public | postlinks | table | btpg10 public | posts | table | btpg10 public | posttypes | table | btpg10 public | users | table | btpg10 public | votes | table | btpg10 public | votetypes | table | btpg10 (9 rows)
Important Considerations:
- Data Type Mapping: Carefully plan data type conversions to avoid data loss or corruption.
- Large Tables: For very large tables, consider using partitioning or other techniques to improve performance.
- Character Encoding: Ensure consistent character encoding between SQL Server and PostgreSQL.
- Transaction Management: Understand how pgloader handles transactions and potential rollback scenarios.
- Error Handling: Implement robust error handling and logging.
- Testing: Thorough testing is crucial at every stage of the migration.
Sirius: Your PostgreSQL Migration Partner
Migrating databases requires careful planning and expertise. Sirius provides comprehensive PostgreSQL migration services to ensure a smooth and successful transition:
- Migration Assessment and Planning: We analyze your current environment and develop a tailored migration strategy.
- pgloader Configuration and Optimization: We expertly configure pgloader to maximize performance and minimize downtime.
- Data Validation and Testing: We ensure data integrity and thorough testing throughout the process.
- Post-Migration Support: We provide ongoing support to optimize your PostgreSQL environment.
Conclusion:
pgloader is a valuable tool for migrating from SQL Server to PostgreSQL. By following best practices and planning carefully, you can achieve a successful migration. Sirius's expertise can further streamline the process and ensure a smooth transition to your new PostgreSQL environment.
Contact Sirius today for a free consultation and discover how we can simplify your SQL Server to PostgreSQL migration. Visit us at [www.siriusopensource.com] to learn more.
















































